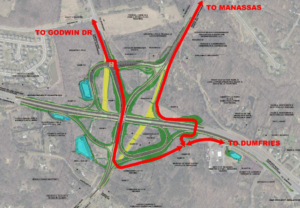
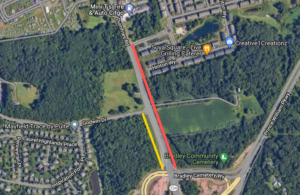
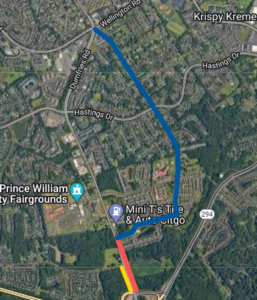
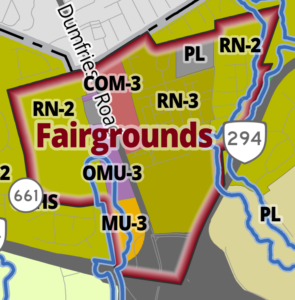
Active Prince William believes that early and proactive community involvement in the development of significant transportation improvement and planning projects would better integrate the community’s needs and preferences into the selection and scope of those projects.
Presently, however, the Prince William Board of County Supervisors (and the local governing bodies for greater Prince William’s cities and towns) routinely endorse staff recommendations for non-local transportation funding requests with minimal public notice or opportunities for citizen comment.
Typically, the public first learns of such funding requests for new transportation projects by discovering them on a Consent Agenda for an upcoming governing body meeting, held before any public comment period. This lack of transparent decision-making, limited public notice, and precluded public comment effectively deprives the public of any opportunity to meaningfully influence the nature and scope of the transportation projects that are advanced for funding.
In the Fall of 2023, we included the following question in our survey for all Prince William Board of County Supervisor candidates:
Question 1: Do you support requiring the PWC [Prince William County] Department of Transportation to hold advertised public hearings before the Board of County Supervisors [BOCS] is scheduled to endorse any future applications for regional (e.g., NVTA, NVTC Commuter Choice), state, or federal transportation improvement funds?
Four of the current BOCS members (Andrea Bailey, Deshundra Jefferson, Bob Weir, and Margaret Franklin) responded “Yes”, three others (Victor Angry, Tom Gordy, and Kenny Boddye) selected “Need more information”, and nobody selected “No”.
To not burden the already-crowded BOCS meeting agendas, this public comment on the County’s proposed new transportation funding requests could be solicited at standalone public meetings or at a scheduled meeting of an appropriate advisory body, such as the Prince William County Planning Commission. Ideally, however, 1) public input would also be solicited online, 2) any staff presentation and advertised public hearing would include a virtual meeting component, and 3) the PWC Department of Transportation would be required to provide both a written summary of the public comments received and a written response to those public comments.
Since non-local transportation funding programs typically have an annual or biennial schedule for new project submissions that is announced many months in advance, the Prince William County Department of Transportation should be able to present all their proposals for new transportation projects being considered in the coming months at one or two consolidated advertised public hearings each year.
We call on the Prince William Board of County Supervisors to issue a directive to the Prince William County Executive with the following components:
- Require the Prince William County Department of Transportation (PWC DOT) to present–for public comment at an advertised public hearing–any proposed first-time request for regional, state, or federal funding for a new transportation or trail capital project or planning activity, in advance of bringing that funding request to the Board of County Supervisors for its endorsement.
- Cite all applicable non-local funding programs, including the Northern Virginia Transportation Authority’s (NVTA) 70% and 30% funds; federal RSTP or CMAQ allocations which are endorsed by the NVTA; the Northern Virginia Transportation Commission’s (NVTC) I-66 and I-95/I-395 Commuter Choice programs; National Capital Region Transportation Planning Board (TPB) technical assistance grants (e.g., Transportation-Land Use Connections, Transit within Reach, Regional Roadway, Safety Program); Transportation Alternatives Set-Aside requests submitted to either the TPB or VDOT; VDOT’s SMART SCALE, Revenue Sharing, and HSIP programs; the Virginia Department of Conservation and Recreation’s Recreational Trails Program; USDOT discretionary grant programs (e.g., RAISE, SS4A); Congressional earmark requests; and the Federal Transit Administration’s Enhanced Mobility Program.
- Allow the PWC DOT to conduct these public hearings at any appropriate venue that includes online viewing and public comment submission components, including at scheduled Planning Commission meetings.
- Specify that the public hearing must be held at least 30 to 60 days before the endorsement request is scheduled to be placed on the BOCS agenda.
- Require the PWC DOT to compile a written summary of–and response to–the public comments received and include that summary with the other BOCS meeting materials when they present their funding request for BOCS approval.
We believe that the process outlined above would provide valuable community input–near the very beginning of the project development process–for both the PWC Department of Transportation and the Board of County Supervisors.